Written by Audrey Wheeler
If one takes Donald Trump’s words at face value, admittedly a dicey proposition, his administration and the anti-conservation majority in the U.S. Congress are likely to launch a volley of assaults on Colorado’s land, water, and climate. And yet, as the state’s largest environmental organization, we remain hopeful for the future. It’s not going to be easy, and the next four years will pose significant challenges to our Colorado values and our outdoor way of life. But we’re going to keep fighting in every way we can — and we know Coloradans stand with us.
First, let’s look at a few of the big challenges we’re facing from our next president:
The concept of global warming was created by and for the Chinese in order to make U.S. manufacturing non-competitive.
— Donald J. Trump (@realDonaldTrump) November 6, 2012
- He’s a climate denier. Someone who has called climate change a “hoax” and may put an oil executive in charge of our public lands does not inspire confidence for leading our country forward with renewable energy and addressing the climate crisis. The President-elect has pledged to roll back environmental laws and regulations that will keep us safe and healthy, from the Clean Power Plan to crucial limits on methane pollution. In Colorado, climate change is projected to cause droughts, hotter temperatures, and health issues, so it’s essential that we act to fight it in any way possible.
- It’s not looking good for land conservation and wildlife protection. We could be facing a four-year “drought” of new protections for land and wildlife across the country. In addition, with an anti-conservation Congress, there are good reasons to be concerned for some of our bedrock environmental laws. This means the Antiquities Act, which was used in Colorado to protect Browns Canyon National Monument, Great Sand Dunes National Park, and Colorado National Monument, could be under threat. Some congressional Republicans have been desperate to roll back key protections in the Endangered Species Act, a bedrock environmental law that protects wildlife.
- Dirty fuels will be promoted. President-elect Trump has pledged to increase dirty energy production, likely by accelerating permitting to drill or frack on our public lands. Colorado has significant coal, oil, and natural gas under our lands so we will need to be on high alert to counter a “drill, baby, drill” mentality.
- The Colorado River is at a critical tipping point. A recent study by the University of Colorado found that the next president must act to prevent widespread water shortages in the Colorado River Basin. A continuing 16-year drought puts the entire Southwestern U.S. in danger of possible water cuts, but so far, Trump has not presented a plan of action.
Of course, none of this is certain. Trump’s candidacy was remarkably policy-free, and when he does talk about policy he frequently contradicts himself with the space of even a few days. All this means there is significant uncertainty about where he stands on key environmental issues. For example, at one point he endorsed local control of oil and gas during a visit to Colorado but it is not clear if he stills holds that view. He has also swayed back and forth on supporting efforts to sell off our public lands, although it’s important to note that the Republican platform contains language supporting this costly and unpopular idea.
At the same time, economic forces beyond the control of the president also provide tremendous uncertainty about the next four years. Oil and natural gas prices, and the impact of natural gas prices on coal, are controlled by the markets. In the past few years, we’ve seen natural gas development outpace coal due in large part to market forces. Even if the president-elect goes all-out to “bring back coal,” he may have little success.
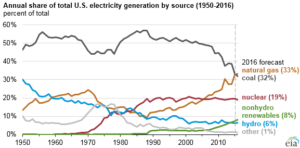
Source: U.S. Energy Information Administration, Monthly Energy Review, and Short-Term Energy Outlook (March 2016)
Meanwhile, renewable energy is booming as wind and solar are becoming more and more affordable. Wind and solar energy already support about 4,250 jobs in Eastern Colorado alone, far exceeding the approximately 1,400 jobs in Colorado’s coal industry.
At Conservation Colorado, we’ve got hope. Our work will continue, and it is more important now than ever.
We’ve got three substantial assets on our side:
Protesters fill the streets in downtown Denver, November 10, 2016
- The will of the people. In Colorado, 77 percent of voters say environmental issues are an important factor in deciding whether to elect a public official. 72 percent of Colorado voters are more likely to vote for a candidate who wants to protect public lands. 76 percent of Colorado voters are more likely to vote for a candidate who wants to promote renewable energy like wind and solar. 77 percent of Colorado voters would rather use water more wisely than divert water from rural rivers. There are more numbers like this, but they all boil down to the same idea: Coloradans have strong conservation values, and want to see them represented in our government. Also, let’s remember, Hillary Clinton beat Donald Trump by 5% here in Colorado — Coloradans did not endorse Trump’s vision for our environmental future.
- Supporters on both sides of the aisle in the state Legislature. We fought for a pro-conservation majority in both the state House and state Senate this year, and we succeeded by expanding our conservation majority in the state House. However, the Senate remains under anti-conservation control. But conservation and the environment are bipartisan issues, and we’ve got several powerful examples of what we can accomplish when our elected officials work across the aisle on environmental issues. Last year with a similarly divided legislature, we scored big by passing electric vehicle tax credits, the first-in-the-nation Colorado Public Lands Day, and legalizing rain barrels. We’re looking forward to more of this bipartisan work in the upcoming year, with opportunities to modernize our transportation system, grow our booming outdoor recreation economy, and further keep Colorado a leader for the nation when it comes to energy and the environment.
- Colorado’s governor is standing up for the environment. In his first post-election interview, Governor John Hickenlooper cited health care, climate action, and public lands as the three main areas of concern for Colorado under President-elect Donald Trump. He vowed that Colorado will continue striving to cut carbon pollution and further clean our air, and will not pull back our strong methane regulations for the oil and gas industry. He also expressed concern for protecting public lands, saying, “Those lands should not be put up for auction.” We’re pleased that the governor is taking a stand and allowing Colorado to chart its own path.
Above all, we will stand together as a community to defend our natural resources and keep up the fight for the future. We’re not alone — a majority of Coloradans share these values and expressed them by voting for pro-conservation candidates in this year’s election.



 So far, scientists haven’t come up with a one-size-fits-all climate change solution for agriculture. But they are constantly looking for and researching new ideas. One of these is a technique called precision agriculture. Raj Kholsa, another CSU researcher, lays precision agriculture out
So far, scientists haven’t come up with a one-size-fits-all climate change solution for agriculture. But they are constantly looking for and researching new ideas. One of these is a technique called precision agriculture. Raj Kholsa, another CSU researcher, lays precision agriculture out  Emissions tests and air pollution limits are in place to protect human health and the air we breathe. Volkswagen’s “too-good-to-be-true” clean diesel cars emitted up to 40 times the legal limit of nitrogen oxides (“NOx”) on the road, but hid these emissions during tests. These smog-forming pollutants, according to
Emissions tests and air pollution limits are in place to protect human health and the air we breathe. Volkswagen’s “too-good-to-be-true” clean diesel cars emitted up to 40 times the legal limit of nitrogen oxides (“NOx”) on the road, but hid these emissions during tests. These smog-forming pollutants, according to