Written by Audrey Wheeler
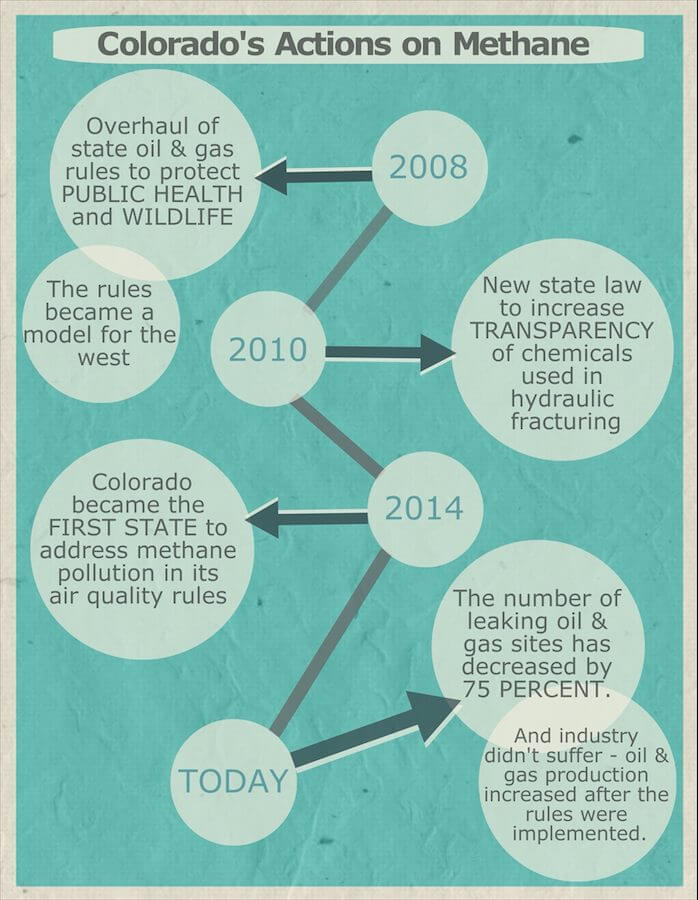
Colorado has long been a leader for the nation in finding policy solutions that strike the right balance between responsible energy development and protecting our clean air, clean water, and treasured lands.
Our state’s past innovation and opportunities for the future were recently highlighted at a panel that Conservation Colorado helped organize in collaboration with the University of Colorado Wirth Chair in Sustainable Development. The full video can be seen here:
The panelists — Dan Grossman, National Director of State Programs, Environmental Defense Fund; Will Allison, Director of the Air Pollution Control Division, Colorado Dept. of Health and Environment; Patrick Von Bargen, Executive Director, Center for Methane Emissions Solutions; Dr. Tanya Heikkila, Professor, CU School of Public Affairs; Jim Armstrong, President, Apogee Scientific — had three major takeaways:
1. Colorado’s methane regulations are good for the economy and the environment
 One in three Americans lives in a county with oil and gas operations, and right now, methane is leaking from over a million oil and gas wells. That’s over 7 million metric tons of methane spilling into the air each year – enough gas to heat 5 million American homes (at a cost of over $1 billion in lost methane).
One in three Americans lives in a county with oil and gas operations, and right now, methane is leaking from over a million oil and gas wells. That’s over 7 million metric tons of methane spilling into the air each year – enough gas to heat 5 million American homes (at a cost of over $1 billion in lost methane).
Methane is the primary component of natural gas, so wasting methane means losing money for oil and gas taxes and royalty revenues. Those lost funds would have supported education, infrastructure such as roads and bridges, and conservation efforts in areas directly affected by energy development. Curbing methane pollution is also critical because it is 80 times more potent than carbon dioxide in the first 20 years after its release, and is already responsible for a quarter of man-made climate change.
The good news is that cleaning up methane waste is a win-win. Oil and gas companies can benefit by bringing more natural gas to market, and entrepreneurs are breaking new ground and creating jobs in an ever-growing methane mitigation industry.
Addressing methane waste helps clean up our air. The same strategies used to cut methane will also help reduce ozone-forming pollutants and toxic emissions such as benzene, which threaten the health of those living closest to development. The Colorado methane rules will be critical to reducing ozone along the Front Range to comply with the new federal ozone standards. As Will Allison, Director, Air Pollution Control Division at the Colorado Department of Public Health and the Environment put it:
“These [regulations] are a good step, but not the end game . . . the EPA recently lowered the health based ozone standard. This makes our challenges here on the Front Range all that much greater.”
Regulations to plug methane leaks are supported by companies in the oil and gas industry. In fact, a recent study by the Center for Methane Emissions Solutions found that representatives from oil and gas companies overwhelmingly agreed that the benefits of Colorado’s regulations outweigh the costs. Companies capture lost product for additional income and reduce emissions without incurring significant costs. Additionally, because of the required inspection schedule, the oil and gas companies have seen improved on-site safety and training for their employees.
2. There is need for more stringent federal regulations
Colorado can’t do it alone. No matter how strong Colorado’s air rules are, we’ll need our neighboring states to match our proactive approach in order to protect our air. As Dr. Tanya Heikkila, Professor at the CU School of Public Affairs, explained:
“We need to find better ways of engaging in productive dialogue and productive policy making [around climate change and methane], and I think Colorado has shown some leadership on this issue – we need to share our lessons beyond our state boundaries.”
Currently, both the U.S. Bureau of Land Management and Environmental Protection Agency are working to cut methane waste and pollution. The BLM has a “no waste” mandate and is responsible for ensuring a fair return to taxpayers when publicly-owned oil and natural gas minerals are developed. The EPA can address methane pollution on state and private lands, which will ensure we don’t leave any loopholes where development takes place.
As Dan Grossman, National Director of State Programs for Oil and Gas at the Environmental Defense Fund described:
“Our Colorado regulations are strong and are working well, but we need to continue to improve them. What I see is a continuing circle of improvement in state and federal regulations so that we can get entire the oil and gas sector under a very cost effective regime that will reduce methane and VOCs across the country.”
3. New technologies can help solve our problems
While hydraulic fracturing is a relatively new system, its widespread use has triggered a response from the industry for methane mitigation and new technologies to reduce pollution.
According to Jim Armstrong, President of Apogee Scientific, “We need have systems that can go out there and economically find larger ‘super emitters’ that may be one hundred times larger than the smaller leaks. We need uniform regulations.” Mr. Armstrong’s company, Apogee, specializes in a new mobile infrared technology that can detect emissions from up to 100 feet away.
And Patrick Von Bargen, Executive Director of the Center for Methane Emissions, discussed a new program through the Department of Energy which has funded research and development on monitoring systems. Their target is to reduce the cost of monitoring leaks by a factor of ten, which will be cost effective and available commercially in two to three years. These new technologies can provide breakthroughs with an enormous reduction of cost.
Colorado’s forward-thinking work on our state rules has provided a model for the nation, and we have proven that methane rules can coexist with responsible energy development. But there is more work to be done, and we need to fight to make it happen.

 What can I use the water for?
What can I use the water for?